Introduction: What is AiOps Automation?
The rapidly growing complexity of modern IT environments—spanning on-premise data centers, multi-cloud deployments, microservices, containers, and edge computing—has pushed traditional IT Operations Management (ITOM) approaches to their limits. This is where AiOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations) comes into play.
AiOps Automation refers to the application of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and advanced analytics to automate, enhance, and optimize IT operations. It helps IT teams correlate massive datasets, detect anomalies, predict failures, and automate responses without requiring constant human oversight.
Key Capabilities of AiOps Automation
- Real-time monitoring and data analysis across hybrid IT environments.
- Anomaly detection using machine learning models trained on historical data.
- Automated incident correlation, prioritization, and resolution.
- Predictive analytics for proactive issue prevention.
- Self-healing systems capable of auto-remediation.
Key Features of AiOps Automation
AiOps Automation offers a comprehensive feature set that transforms the way IT operations are managed. These features combine AI intelligence with IT operations processes to deliver a seamless, proactive, and efficient IT environment.
Core Features of AiOps Automation
- Data Aggregation and Normalization
- Collects structured and unstructured data from diverse sources including logs, events, metrics, and traces.
- Standardizes data for cross-platform correlation and analysis.
- Pattern Recognition and Anomaly Detection
- Identifies trends, performance deviations, and behavioral anomalies.
- Learns “normal” system behavior and detects deviations in real-time.
- Automated Incident Management
- Correlates multiple alerts into a single incident timeline.
- Automatically classifies and prioritizes incidents based on business impact.
- Predictive Analytics and Forecasting
- Forecasts capacity issues, performance bottlenecks, and potential failures before they occur.
- Suggests preemptive actions based on historical data and trends.
- Automated Remediation and Self-Healing
- Triggers pre-defined remediation workflows to resolve known issues.
- Implements self-healing actions without human intervention.
Benefits of AiOps Automation in IT Operations
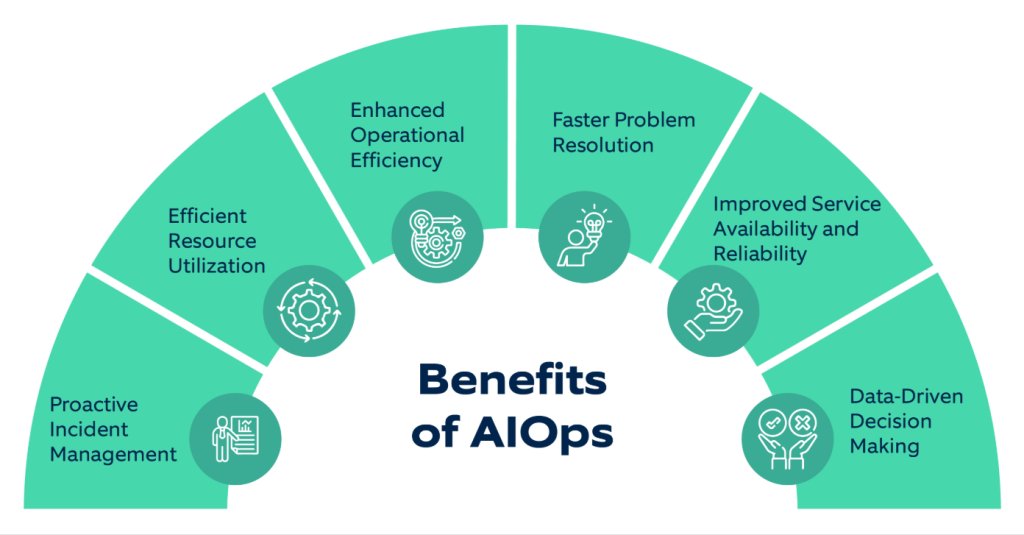
The adoption of AiOps is driving significant improvements in IT operations across organizations, especially those managing hybrid and multi-cloud environments. AiOps Automation enhances efficiency, reliability, and responsiveness, positioning IT teams to better support business needs.
Key Benefits of AiOps Automation
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity
- Reduces the manual effort required for monitoring, incident management, and troubleshooting.
- Automates repetitive tasks, freeing up IT staff for strategic work.
- Enhanced Service Reliability
- Identifies potential service disruptions before they impact users.
- Enables proactive fixes and faster incident response.
- Reduced Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR)
- Automatically correlates logs, events, and performance data to pinpoint root causes.
- Provides actionable insights to speed up resolution.
- Cost Optimization
- Optimizes resource utilization and cloud spending by identifying underused resources.
- Reduces operational costs through automated processes and fewer manual interventions.
- Cross-Team Collaboration
- Provides a single-pane-of-glass view of IT health for all stakeholders.
- Enhances collaboration between IT Operations, DevOps, and Security teams.
Use Cases: How AiOps Automation is Transforming IT
AiOps is not limited to infrastructure monitoring—it spans applications, networks, security, and business services. These real-world use cases illustrate how AiOps Automation is reshaping IT operations:
Common Use Cases of AiOps Automation
- Infrastructure Monitoring and Management
- Monitors servers, networks, databases, and cloud platforms in real-time.
- Detects configuration drift and automates remediation actions.
- Application Performance Management (APM)
- Tracks application performance, user experience, and response times.
- Identifies bottlenecks at the code, middleware, or infrastructure level.
- Proactive Incident Prevention
- Learns from historical incidents to predict and prevent future problems.
- Identifies recurring issues and recommends permanent fixes.
- Automated Security Incident Response
- Detects anomalous network traffic or access patterns.
- Integrates with SIEM systems to trigger automated containment and response workflows.
- Cloud Cost Optimization
- Analyzes multi-cloud consumption patterns and identifies cost-saving opportunities.
- Automates the shutdown of idle resources and rightsizing of over-provisioned services.
Challenges in Implementing AiOps Automation
Despite its potential, adopting AiOps Automation comes with its own set of challenges. Organizations need to carefully plan their AiOps strategy to avoid common pitfalls and ensure successful deployment.
Key Challenges in AiOps Adoption
- Data Silos and Integration Issues
- Aggregating data from legacy, cloud-native, and third-party systems.
- Ensuring data consistency across different formats and platforms.
- Model Accuracy and Drift
- Ensuring AI models remain accurate as systems, applications, and infrastructure evolve.
- Continuously retraining models with new data and evolving patterns.
- Resistance to Change
- Overcoming the cultural shift from manual IT operations to automated, AI-driven processes.
- Ensuring IT teams are trained in AiOps tools and processes.
- Privacy, Compliance, and Security Concerns
- Managing sensitive data in compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulations.
- Ensuring AiOps platforms adhere to security best practices.
- Vendor Lock-In Risks
- Choosing platforms that support open APIs and multi-cloud environments.
- Avoiding reliance on proprietary models and data formats.
The Future of AiOps Automation
As IT landscapes become more complex, AiOps Automation will evolve into an even more powerful enabler of autonomous IT operations, predictive service management, and business agility. The future will be shaped by:
Emerging Trends in AiOps
- Hyperautomation Across ITSM and ITOM
- Combining AiOps with IT Service Management (ITSM) for fully automated incident detection, classification, and resolution.
- Generative AI for Knowledge Management
- Using GenAI to generate root cause analyses, playbooks, and remediation steps based on historical data.
- Digital Twins for IT Operations
- Creating digital twins of IT environments to simulate performance under various scenarios and predict the impact of changes.
- Unified Observability with AiOps
- Integrating AiOps with Observability platforms to provide full-stack visibility across infrastructure, applications, and user experiences.
- Autonomous IT Operations (NoOps)
- Moving closer to a self-managing IT environment where AiOps not only detects and resolves issues but also self-optimizes infrastructure.
