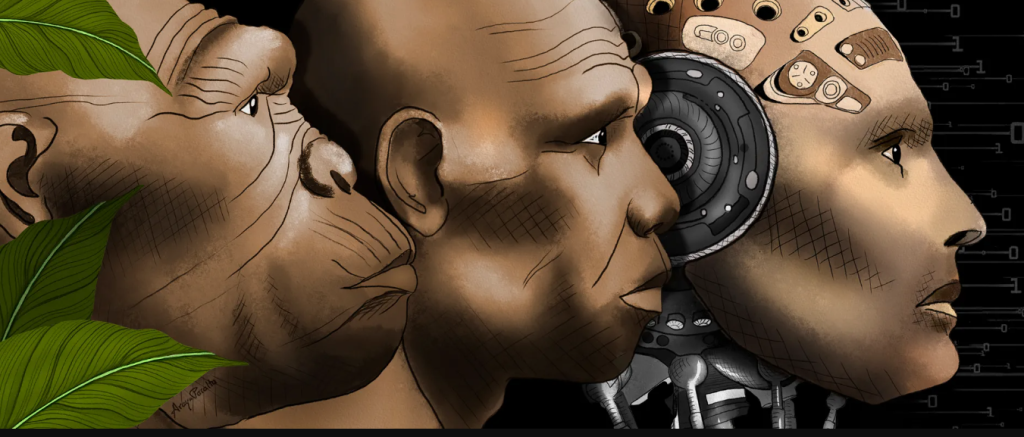

Section 1: Introduction to Transhumanism
Definition and Overview
What is Transhumanism?
Transhumanism is an intellectual and cultural movement that advocates for the use of technology to enhance the human condition. It seeks to transcend the biological limitations of humans through advanced technologies, aiming to improve physical and cognitive abilities, extend lifespan, and enhance overall well-being. Transhumanism envisions a future where humans evolve into “posthumans” with capabilities far beyond current limitations. This movement encourages the exploration of innovative technologies, such as genetic engineering, artificial intelligence, and nanotechnology, to redefine what it means to be human.
Historical Background and Origins
The roots of transhumanism can be traced back to ancient myths and legends that envisioned humans achieving immortality and divine powers. However, the modern transhumanist movement began to take shape in the 20th century, influenced by the rapid advancements in science and technology. Notable figures such as Julian Huxley, who coined the term “transhumanism” in the 1950s, and futurists like F.M. Esfandiary (FM-2030) and Max More, have played key roles in developing transhumanist thought. The publication of seminal works like “The Singularity is Near” by Ray Kurzweil has further popularized transhumanism, highlighting the potential of exponential technological growth to transform human life.

Key Concepts and Terminology
Transhumanism involves several core concepts, including enhancement, singularity, and posthumanism. Enhancement refers to the use of technology to improve human abilities, such as intelligence, strength, and longevity. The singularity is a hypothetical future point where technological growth becomes uncontrollable and irreversible, resulting in profound changes to civilization. Posthumanism envisions a future where humans have evolved into beings with vastly superior capabilities, transcending current biological and cognitive limitations. These concepts form the foundation of transhumanist philosophy and guide its pursuit of technological progress.
Philosophical Foundations
Humanism and Posthumanism
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the value and agency of human beings, focusing on reason, ethics, and the pursuit of knowledge. Transhumanism builds upon humanist principles by advocating for the use of technology to enhance human potential and address fundamental human challenges. Posthumanism extends this idea by envisioning a future where humans evolve into new forms of life with capabilities beyond current human limitations. This shift challenges traditional notions of human identity and raises questions about what it means to be human.
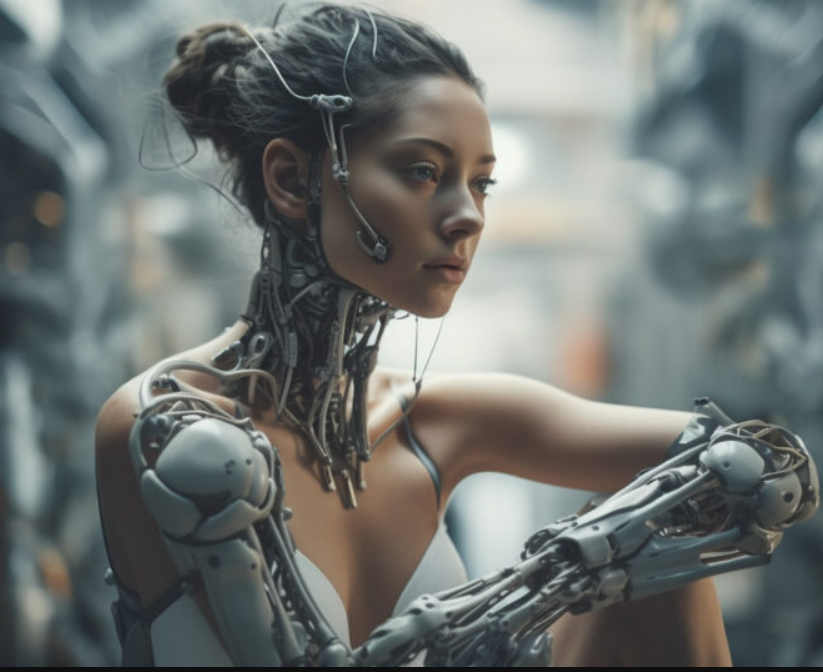

Philosophers and Thinkers of Transhumanism
Transhumanism has been shaped by a diverse array of thinkers and philosophers who have explored its ethical, philosophical, and practical implications. Notable figures include Max More, who founded the Extropy Institute and articulated the principles of transhumanism, and Nick Bostrom, whose work on existential risks and human enhancement has informed the movement’s ethical considerations. Other influential thinkers, such as Anders Sandberg and Natasha Vita-More, have contributed to transhumanist discourse by examining the social and cultural impact of emerging technologies.
Core Principles and Beliefs
Transhumanism is guided by several core principles and beliefs, including the pursuit of progress, the ethical use of technology, and the importance of individual autonomy. Transhumanists advocate for open access to enhancement technologies and emphasize the need for responsible development to mitigate potential risks. The movement also promotes the idea that individuals should have the freedom to choose whether and how to enhance themselves, while recognizing the broader societal implications of these choices. By embracing these principles, transhumanism seeks to create a future where technology empowers individuals and improves the human condition.
Section 2: Technologies Enabling Transhumanism
Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering

CRISPR and Gene Editing
CRISPR-Cas9 is a revolutionary gene-editing technology that allows precise modifications to DNA sequences. This tool enables scientists to edit genes within living organisms, offering the potential to correct genetic disorders, enhance desirable traits, and eliminate disease-causing mutations. CRISPR has accelerated advancements in genetic engineering and personalized medicine, providing a powerful platform for human enhancement. Its applications range from treating genetic diseases like cystic fibrosis and muscular dystrophy to developing crops with improved nutritional content and resistance to pests.
Synthetic Biology and Genetic Enhancement
Synthetic biology involves designing and constructing new biological parts and systems or redesigning existing ones for useful purposes. By combining genetic engineering with synthetic biology, scientists can create organisms with novel functions and enhance human traits such as intelligence, strength, and resilience. Genetic enhancement raises ethical questions about the potential for eugenics and social inequality, but it also offers opportunities to address pressing health challenges and improve quality of life. Advances in synthetic biology could lead to breakthroughs in regenerative medicine, biofabrication, and sustainable agriculture.
Anti-Aging and Longevity Research
Transhumanism envisions extending human lifespan through advances in biotechnology and medicine. Anti-aging research focuses on understanding the biological mechanisms of aging and developing interventions to slow, halt, or reverse age-related decline. Scientists are exploring approaches such as senolytics, which target senescent cells that contribute to aging, and telomere extension, which aims to preserve chromosomal integrity. Longevity research also investigates the role of metabolism, caloric restriction, and autophagy in promoting healthy aging. While significant challenges remain, the pursuit of increased longevity aligns with transhumanist goals of enhancing human health and vitality.
Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence
AI and Machine Learning in Human Enhancement
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming transhumanism by enabling the development of intelligent systems that can augment human capabilities. AI-driven technologies, such as natural language processing and computer vision, enhance cognitive functions, providing tools for real-time translation, data analysis, and decision-making. Machine learning algorithms personalize user experiences, adapting to individual preferences and optimizing outcomes. AI’s integration with transhumanism raises ethical considerations related to privacy, bias, and autonomy, necessitating responsible development and deployment.
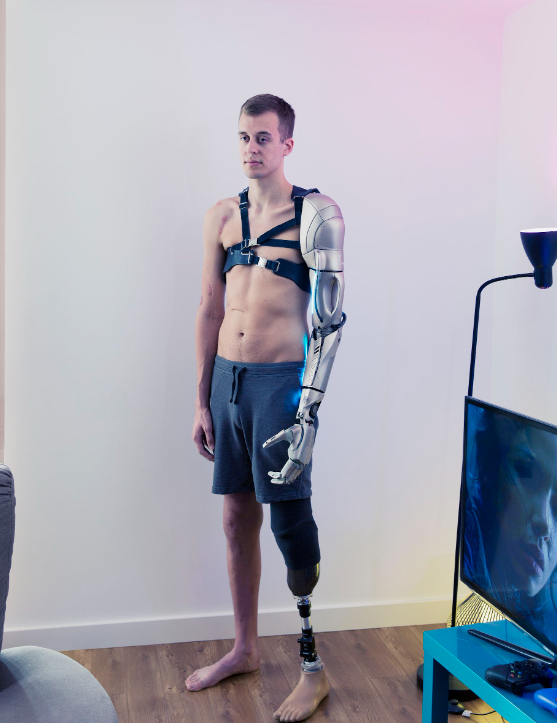
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs)
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are technologies that facilitate direct communication between the brain and external devices. BCIs have the potential to revolutionize human-computer interaction, allowing individuals to control machines using their thoughts. This technology has applications in assistive devices for individuals with disabilities, cognitive enhancement, and virtual reality. BCIs enable the development of neural prosthetics, which can restore motor functions or enhance sensory perception. However, ethical concerns regarding privacy, security, and consent must be addressed to ensure the responsible use of BCIs in transhumanist applications.
The Role of Big Data in Personalization and Prediction
Big data analytics plays a crucial role in transhumanism by enabling the analysis of vast amounts of information to personalize and optimize human experiences. By harnessing data from wearable devices, social media, and medical records, transhumanist technologies can provide tailored recommendations for health, lifestyle, and education. Predictive analytics can identify trends and patterns, enabling proactive decision-making and intervention. While big data offers opportunities for human enhancement, it also raises concerns about data privacy, consent, and the potential for surveillance.
Nanotechnology and Materials Science
Nanobots and Medical Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology involves manipulating matter at the atomic and molecular scale to create materials and devices with novel properties. In medicine, nanobots—tiny robotic devices—can be designed to perform tasks within the human body, such as targeted drug delivery, tissue repair, and diagnostics. Medical nanotechnology has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by providing precise and minimally invasive treatments, enhancing the efficacy and safety of interventions. However, the development of nanobots raises ethical questions about safety, control, and the unintended consequences of manipulating biological systems at the nanoscale.
Smart Materials and Wearable Tech
Smart materials and wearable technologies are integral to transhumanism, offering new ways to enhance human capabilities and monitor health. Smart materials, such as shape-memory alloys and conductive polymers, can change properties in response to external stimuli, enabling the development of adaptive devices and prosthetics. Wearable technologies, including fitness trackers and augmented reality glasses, provide real-time data on physical activity, health metrics, and environmental conditions. These technologies empower individuals to take control of their health and well-being, but they also require careful consideration of data security and user privacy.
Energy Solutions and Environmental Impact
Nanotechnology and materials science are driving innovations in energy solutions, contributing to sustainable and efficient resource use. Advances in solar cells, batteries, and fuel cells enhance energy production and storage, supporting the transition to renewable energy sources. Transhumanism emphasizes the importance of minimizing environmental impact and addressing global challenges such as climate change and resource depletion. By developing technologies that optimize energy use and reduce waste, transhumanism seeks to create a future where technological progress aligns with environmental stewardship.
Robotics and Cybernetics
Prosthetics and Bionic Limbs
Advancements in robotics and cybernetics have led to the development of sophisticated prosthetics and bionic limbs that restore or enhance human abilities. These devices integrate sensors, actuators, and control systems to mimic natural limb function, enabling individuals with limb loss to regain mobility and dexterity. Innovations in neural interfaces allow users to control bionic limbs using their thoughts, providing a seamless and intuitive experience. The development of prosthetics and bionic limbs raises ethical considerations related to accessibility, equity, and the potential for human augmentation beyond natural abilities.
Human Augmentation through Robotics
Robotics offers opportunities for human augmentation, enhancing physical capabilities and extending human potential. Exoskeletons and powered suits assist with heavy lifting and mobility, improving workplace safety and productivity. Robotic systems can also augment sensory perception, enabling individuals to perceive environmental changes or detect hidden objects. While robotic augmentation offers benefits for individuals and society, it also presents ethical challenges related to the implications of enhancing human capabilities and the potential for inequality.
The Integration of Humans and Machines
The integration of humans and machines represents a key aspect of transhumanism, where technology becomes an extension of the human body and mind. This integration blurs the boundaries between biology and technology, enabling new forms of interaction and expression. The development of cybernetic systems raises philosophical questions about identity, agency, and the definition of humanity. Ensuring that the integration of humans and machines aligns with ethical principles and respects individual autonomy is critical for the responsible advancement of transhumanism.
Section 3: Applications and Implications of Transhumanism
Health and Medicine
Personalized Medicine and Genomics
Personalized medicine leverages genetic information to tailor medical treatments and interventions to individual patients. By analyzing genomic data, healthcare providers can identify genetic predispositions to diseases, optimize drug therapies, and develop targeted treatments. Personalized medicine aligns with transhumanist goals by enhancing healthcare outcomes and improving quality of life. However, ethical considerations related to data privacy, consent, and access to genetic information must be addressed to ensure the equitable and responsible implementation of personalized medicine.
Advanced Prosthetics and Rehabilitation
Transhumanism is driving innovations in advanced prosthetics and rehabilitation technologies, enabling individuals with disabilities to regain function and independence. Robotic prosthetics with neural interfaces provide intuitive control and feedback, while virtual reality and neurofeedback enhance rehabilitation outcomes. These technologies empower individuals to overcome physical limitations, but they also raise ethical questions about accessibility, affordability, and the potential for augmentation beyond natural abilities.
Brain Enhancement and Cognitive Augmentation
Transhumanism envisions the enhancement of cognitive abilities through technologies such as nootropics, neurostimulation, and brain-computer interfaces. Cognitive augmentation aims to improve memory, attention, and problem-solving skills, offering opportunities for personal and professional growth. While cognitive enhancement holds promise for enhancing human potential, it also presents ethical challenges related to fairness, consent, and the potential for unintended consequences. Ensuring that cognitive enhancement technologies are developed and used responsibly is critical for maximizing their benefits and minimizing risks.
Society and Culture
Impact on Work and Employment
Transhumanism is transforming the nature of work and employment, with automation and AI reshaping industries and labor markets. As machines take on routine and repetitive tasks, humans are freed to focus on creative and strategic roles. This shift offers opportunities for increased productivity and innovation, but it also presents challenges related to job displacement and workforce re-skilling. Transhumanism emphasizes the importance of preparing for these changes by fostering a culture of lifelong learning and adaptability, ensuring that individuals can thrive in an evolving economic landscape.
Education and Lifelong Learning
The integration of technology into education is a key aspect of transhumanism, offering new opportunities for personalized and immersive learning experiences. AI-driven platforms provide tailored educational content and feedback, while virtual and augmented reality create interactive and engaging learning environments. Transhumanism advocates for the democratization of education, ensuring that individuals have access to the resources and opportunities needed to achieve their potential. Lifelong learning is emphasized as a means of adapting to technological change and maintaining relevance in a rapidly evolving world.
Cultural Shifts and Human Identity
Transhumanism challenges traditional notions of human identity and culture, as technology reshapes the boundaries of what it means to be human. The integration of technology into daily life raises questions about authenticity, agency, and the nature of human experience. Transhumanism encourages exploration of new forms of identity and expression, while emphasizing the importance of preserving cultural diversity and heritage. Engaging in open dialogue about the cultural implications of transhumanism is essential for fostering understanding and acceptance of technological change.
Economics and Politics
Economic Impacts of Human Enhancement
Transhumanism has the potential to drive economic growth by increasing productivity, extending working life, and fostering innovation. Human enhancement technologies can improve workforce capabilities and create new industries, generating economic opportunities and prosperity. However, the distribution of economic benefits and the potential for inequality must be addressed to ensure that the advantages of transhumanism are shared equitably. Policymakers and stakeholders must collaborate to develop strategies that maximize economic benefits while minimizing disparities.
Policy and Regulation of Transhumanist Technologies
The regulation of transhumanist technologies is a complex and evolving challenge, as policymakers navigate the balance between innovation and oversight. Developing flexible and adaptive regulatory frameworks that address ethical, safety, and privacy concerns is critical for the responsible deployment of enhancement technologies. Collaboration between governments, industry, and civil society is essential for establishing international standards and guidelines that ensure the safe and equitable use of transhumanist technologies.
The Future of Democracy and Governance
Transhumanism has the potential to reshape governance and democratic processes by enabling new forms of participation and decision-making. Digital technologies can enhance transparency, accountability, and citizen engagement, empowering individuals to influence policy and governance. However, the concentration of technological power and the potential for surveillance raise concerns about individual autonomy and civil liberties. Ensuring that the principles of democracy and human rights are upheld in the context of transhumanism is essential for fostering a fair and inclusive society.
Ethical and Moral Considerations
Equity and Access to Enhancements
Ensuring equitable access to enhancement technologies is a fundamental ethical consideration for transhumanism. Disparities in access to technology can exacerbate existing social inequalities and create new divisions between enhanced and non-enhanced individuals. Transhumanism advocates for the democratization of technology, emphasizing the importance of accessibility, affordability, and inclusivity. Policies and initiatives that promote equitable access to enhancements are essential for realizing the potential of transhumanism to improve human well-being.
Ethical Concerns in Genetic Modification
The genetic modification of humans raises profound ethical questions about the nature of humanity, individual rights, and the potential for unintended consequences. Concerns about eugenics, consent, and the manipulation of human traits require careful consideration and oversight. Transhumanism emphasizes the importance of ethical guidelines and governance structures that ensure the responsible development and use of genetic technologies, balancing innovation with respect for human dignity and diversity.
Privacy and Surveillance in a Transhumanist Society
The integration of technology into human life raises concerns about privacy, surveillance, and the potential for misuse of personal data. Transhumanism advocates for the development of technologies that respect individual privacy and autonomy while enabling new forms of interaction and expression. Ensuring that data protection and security measures are in place is essential for fostering trust and acceptance of transhumanist technologies. Engaging in dialogue about the ethical implications of surveillance and data use is critical for shaping a future where technology empowers individuals rather than undermines their rights.
Section 4: Challenges and Criticisms of Transhumanism
Technical and Scientific Limitations
Current Limitations of Enhancements
Despite the potential of transhumanist technologies, significant technical and scientific challenges remain. Current limitations include the complexity of biological systems, the variability of human response to enhancements, and the potential for unintended side effects. Overcoming these challenges requires continued research and innovation, as well as interdisciplinary collaboration between scientists, engineers, and ethicists. Addressing technical limitations is essential for realizing the promise of transhumanism and ensuring that enhancement technologies are safe and effective.
Potential Risks and Unintended Consequences
The development and deployment of enhancement technologies carry inherent risks and uncertainties. Potential unintended consequences include genetic mutations, environmental impact, and the disruption of ecosystems. Transhumanism emphasizes the importance of risk assessment, monitoring, and mitigation strategies to minimize negative outcomes and ensure the responsible use of technology. Engaging in ethical reflection and dialogue about the potential risks and benefits of enhancements is critical for guiding the development of transhumanist technologies.
Scientific Skepticism and Debate
Transhumanism is a subject of ongoing scientific skepticism and debate, with questions about the feasibility, safety, and ethical implications of enhancement technologies. Critics argue that transhumanism may overestimate the potential of technology to solve complex human challenges and underestimate the importance of social and cultural factors. Engaging in open and rigorous debate about the scientific and ethical dimensions of transhumanism is essential for advancing knowledge and fostering responsible innovation.
Social and Ethical Challenges
Social Inequality and the Digital Divide
Transhumanism has the potential to exacerbate social inequalities and create new divides between those with access to enhancement technologies and those without. The digital divide, characterized by disparities in access to technology and information, poses a significant challenge to the equitable distribution of the benefits of transhumanism. Addressing social inequality and promoting digital inclusion are essential for ensuring that the advantages of enhancement technologies are shared broadly and fairly.
Ethical Dilemmas in Human Enhancement
The pursuit of human enhancement raises ethical dilemmas related to consent, autonomy, and the potential for coercion. Questions about the fairness and desirability of enhancing human traits, such as intelligence or physical abilities, require careful consideration and ethical reflection. Transhumanism advocates for the development of ethical guidelines and frameworks that address these dilemmas, ensuring that enhancement technologies are used responsibly and in alignment with societal values.
Public Perception and Acceptance
The acceptance and adoption of transhumanist technologies depend on public perception and trust. Concerns about the potential risks, ethical implications, and societal impact of enhancements influence public attitudes and acceptance. Engaging with the public through education, dialogue, and transparency is essential for fostering understanding and trust in transhumanist technologies. Addressing misconceptions and fears is critical for building a foundation of support and acceptance for the responsible use of enhancement technologies.
Philosophical and Existential Concerns
Identity and the Definition of Humanity
Transhumanism challenges traditional notions of identity and the definition of humanity by envisioning a future where humans transcend their biological limitations. Questions about what it means to be human, the nature of consciousness, and the continuity of personal identity are central to philosophical debates about transhumanism. Engaging in philosophical reflection about the implications of enhancement technologies for human identity and agency is essential for guiding the development of transhumanist innovations.
The Concept of Mortality and Immortality
The pursuit of immortality and the extension of human lifespan are central goals of transhumanism, raising philosophical questions about the nature of mortality and the value of human life. The desire to overcome aging and death challenges traditional views of human existence and the meaning of life. Engaging in philosophical dialogue about the implications of immortality and longevity is critical for understanding the potential impact of transhumanist technologies on human values and experiences.
The Risk of Technological Determinism
Transhumanism’s emphasis on technological progress and human enhancement raises concerns about technological determinism, the belief that technology determines the course of human history and social development. Critics argue that technological determinism overlooks the importance of human agency, culture, and ethics in shaping the future. Engaging in critical reflection about the role of technology in society is essential for ensuring that transhumanist innovations align with human values and aspirations.
Section 5: Future Trends and Scenarios
The Future of Human Evolution
Predicting Human Evolutionary Pathways
Transhumanism envisions a future where humans actively shape their own evolutionary pathways through enhancement technologies. Predicting the direction of human evolution involves exploring the potential impact of genetic engineering, AI, and other technologies on human traits and capabilities. While the future of human evolution remains uncertain, transhumanism emphasizes the importance of responsible innovation and ethical reflection in guiding the development of enhancement technologies.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Humanity
Technology plays a central role in shaping the future of humanity, influencing how individuals interact, learn, and work. Transhumanism envisions a future where technology empowers individuals to transcend biological limitations and achieve new levels of creativity, intelligence, and well-being. Ensuring that technology aligns with human values and aspirations is critical for fostering a future where technological progress enhances the human condition.
Scenarios of Posthumanism
Posthumanism envisions a future where humans evolve into beings with capabilities beyond current biological and cognitive limitations. Scenarios of posthumanism explore the potential impact of enhancement technologies on human identity, society, and culture. Engaging in dialogue about the implications of posthumanism is essential for understanding the potential benefits and risks of transcending human limitations and guiding the development of transhumanist technologies.
Utopian and Dystopian Visions
Utopian Futures and the Promise of Transhumanism
Transhumanism envisions utopian futures where technology enhances human capabilities, eliminates suffering, and creates a society of abundance and opportunity. Utopian visions highlight the potential benefits of transhumanism, including improved health, extended lifespan, and enhanced creativity. While these visions inspire hope and optimism, they also require careful consideration of the ethical and social implications of enhancement technologies to ensure that the benefits of transhumanism are realized for all.
Dystopian Risks and the Precautionary Principle
Dystopian visions of transhumanism emphasize the potential risks and challenges of enhancement technologies, including social inequality, loss of privacy, and the erosion of human values. The precautionary principle, which advocates for caution and risk assessment in the face of uncertainty, is essential for addressing potential dystopian outcomes and ensuring the responsible development and use of transhumanist technologies. Engaging in dialogue about the potential risks and benefits of enhancement technologies is critical for balancing optimism with caution and fostering a future that aligns with human values.
Balancing Optimism with Caution
Transhumanism encourages a balance between optimism and caution in the pursuit of technological progress and human enhancement. While the potential benefits of enhancement technologies are significant, they also require careful consideration of ethical, social, and environmental implications. Engaging in dialogue about the potential risks and benefits of transhumanism is essential for fostering responsible innovation and ensuring that technological progress aligns with human values and aspirations.
Transhumanism and Space Exploration
The Role of Transhumanism in Space Colonization
Transhumanism envisions a future where enhancement technologies enable humans to explore and colonize space, expanding the boundaries of human existence beyond Earth. By addressing the physical and psychological challenges of space travel, transhumanism offers opportunities for humans to thrive in extraterrestrial environments. The development of transhumanist technologies for space exploration requires collaboration between scientists, engineers, and policymakers to ensure that space colonization aligns with ethical principles and human values.
Enhancements for Space Travel and Survival
Enhancement technologies play a critical role in enabling humans to survive and thrive in the harsh conditions of space. Genetic modifications, AI-driven systems, and nanotechnology can enhance physical resilience, cognitive abilities, and adaptability, improving the prospects for long-term space missions and colonization. Ensuring that these enhancements are developed and used responsibly is essential for maximizing their benefits and minimizing risks.
Transhumanism as a Driver for Space Exploration
Transhumanism’s emphasis on human enhancement and technological progress aligns with the goals of space exploration, offering opportunities for collaboration and innovation. By addressing the challenges of space travel and colonization, transhumanism contributes to the advancement of human knowledge and the expansion of human presence beyond Earth. Ensuring that the pursuit of space exploration aligns with ethical principles and human values is essential for fostering a future where technological progress enhances the human condition.
Section 6: Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Innovative Projects and Companies
Leading Companies in Human Enhancement
Several companies are at the forefront of developing enhancement technologies that align with transhumanist goals. Companies like Neuralink and OpenAI are pioneering advancements in brain-computer interfaces and artificial intelligence, while others like CRISPR Therapeutics and Calico are driving innovations in genetic engineering and longevity research. These companies contribute to the advancement of transhumanism by developing technologies that enhance human capabilities and improve quality of life.
Breakthrough Projects in Transhumanist Research
Breakthrough projects in transhumanist research demonstrate the potential of enhancement technologies to transform human life. Notable projects include the development of advanced prosthetics with neural interfaces, personalized medicine platforms that leverage genomic data, and AI-driven systems that enhance cognitive abilities. These projects showcase the potential of transhumanist technologies to address fundamental human challenges and improve well-being.
Success Stories and Failures
The history of transhumanism is marked by both success stories and failures, offering valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities of enhancement technologies. Success stories highlight the potential of transhumanist technologies to improve health, extend lifespan, and enhance human capabilities, while failures underscore the importance of ethical reflection, risk assessment, and responsible innovation. Engaging in dialogue about the successes and failures of transhumanism is essential for guiding the development of enhancement technologies and fostering a future that aligns with human values.
Biographical Profiles of Key Figures
Influential Transhumanist Thinkers and Leaders
Transhumanism has been shaped by a diverse array of thinkers and leaders who have explored its ethical, philosophical, and practical implications. Notable figures include Max More, who founded the Extropy Institute and articulated the principles of transhumanism, and Nick Bostrom, whose work on existential risks and human enhancement has informed the movement’s ethical considerations. Other influential thinkers, such as Anders Sandberg and Natasha Vita-More, have contributed to transhumanist discourse by examining the social and cultural impact of emerging technologies.
Entrepreneurs and Innovators in Transhumanism
Entrepreneurs and innovators play a critical role in advancing transhumanism by developing technologies that enhance human capabilities and improve quality of life. Visionary leaders like Elon Musk, who founded Neuralink, and Ray Kurzweil, a prominent futurist and advocate for the singularity, have driven advancements in AI, biotechnology, and brain-computer interfaces. These innovators contribute to the growth and impact of transhumanism by pushing the boundaries of technological progress and exploring new possibilities for human enhancement.
Profiles of Prominent Critics and Opponents
Transhumanism has also faced criticism and opposition from individuals who raise ethical, philosophical, and social concerns about enhancement technologies. Critics like Francis Fukuyama, who has expressed concerns about the implications of biotechnology for human nature, and Bill McKibben, an environmentalist who advocates for caution in the pursuit of technological progress, offer valuable perspectives on the potential risks and challenges of transhumanism. Engaging in dialogue with critics and opponents is essential for fostering a balanced and informed understanding of transhumanism and its implications.
Section 7: Resources and Further Reading
Books and Articles
Foundational Texts in Transhumanism
Several foundational texts provide insights into the principles, philosophy, and implications of transhumanism. Notable works include “The Singularity is Near” by Ray Kurzweil, which explores the potential of exponential technological growth, and “Transhumanist Reader” edited by Max More and Natasha Vita-More, which offers a comprehensive overview of transhumanist thought. These texts serve as valuable resources for understanding the foundations of transhumanism and its potential impact on humanity.
Recent Publications and Reviews
Recent publications and reviews highlight the latest advancements, challenges, and ethical considerations in transhumanism. Books such as “Homo Deus: A Brief History of Tomorrow” by Yuval Noah Harari and “Superintelligence: Paths, Dangers, Strategies” by Nick Bostrom explore the implications of enhancement technologies for the future of humanity. Engaging with recent literature is essential for staying informed about the evolving landscape of transhumanism and its potential impact on society.
Essential Articles and Papers
A wealth of articles and papers explore the diverse dimensions of transhumanism, offering insights into its philosophical, ethical, and practical implications. Journals such as “Journal of Evolution and Technology” and “Futures” publish research and reviews on topics related to transhumanism, including human enhancement, AI, and biotechnology. Engaging with scholarly articles and papers is essential for deepening understanding and fostering informed dialogue about transhumanism.
Documentaries and Media
Recommended Films and Documentaries
Films and documentaries offer engaging and thought-provoking perspectives on transhumanism and its implications. Notable documentaries include “Transcendent Man,” which explores Ray Kurzweil’s vision of the singularity, and “Human Nature,” which examines the potential of CRISPR technology to transform humanity. These films provide valuable insights into the opportunities and challenges of transhumanism, encouraging reflection and dialogue about its implications for the future.
Podcasts and Interviews
Podcasts and interviews offer accessible and informative discussions on topics related to transhumanism, providing insights from experts, thinkers, and innovators. Notable podcasts include “Singularity.FM,” which features interviews with leading figures in transhumanism, and “Future Grind,” which explores the intersection of technology and society. Engaging with podcasts and interviews is a valuable way to stay informed about the latest developments and debates in transhumanism.
Online Media and Educational Resources
Online media and educational resources offer a wealth of information on transhumanism, providing opportunities for learning and engagement. Websites such as “H+ Magazine” and “Transhumanist Party” offer news, articles, and resources related to transhumanism and human enhancement. Engaging with online media and educational resources is essential for staying informed and participating in the global conversation about transhumanism and its implications.
Organizations and Communities
Key Transhumanist Organizations and Networks
Several organizations and networks are dedicated to advancing the goals and principles of transhumanism. Notable organizations include the Humanity+ (formerly the World Transhumanist Association), which promotes the ethical use of technology to enhance human capabilities, and the Singularity University, which fosters innovation and collaboration to address global challenges. These organizations provide opportunities for engagement, collaboration, and advocacy, contributing to the growth and impact of transhumanism.
Conferences and Events
Conferences and events offer valuable opportunities for networking, learning, and collaboration within the transhumanist community. Notable events include the TransVision Conference, which brings together thinkers, innovators, and advocates to explore the future of humanity and technology, and the Singularity Summit, which focuses on the implications of exponential technological growth. Engaging with conferences and events is essential for staying informed about the latest developments and trends in transhumanism.
Online Communities and Forums
Online communities and forums provide platforms for discussion, collaboration, and engagement with others interested in transhumanism and human enhancement. Websites such as Reddit’s r/Transhumanism and the Transhumanist Forum offer opportunities for dialogue and exchange of ideas, fostering a sense of community and connection. Participating in online communities and forums is a valuable way to engage with diverse perspectives and contribute to the global conversation about transhumanism.
